In today's rapidly evolving world, the Internet of Things (IoT) plays a crucial role in connecting devices and simplifying our lives. Among the many tools available for IoT development, Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT has emerged as a powerful solution for enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT allows users to manage and control IoT devices remotely, making it an ideal choice for both small-scale and large-scale projects. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional developer, this technology offers unparalleled flexibility and scalability.
This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT, from its basic functionality to advanced implementation techniques. By the end of this article, you'll have a thorough understanding of how to leverage this tool effectively.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
- Understanding Raspberry Pi Basics
- What is RemoteIoT?
- Setting Up Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
- Applications of Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
- Security Considerations in Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
- Optimizing Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT Performance
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Essential Tools for Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
- The Future of Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
Introduction to Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT has become a game-changer in the IoT industry, offering users the ability to manage their devices from virtually anywhere. This technology combines the power of Raspberry Pi with the convenience of remote access, enabling seamless integration of hardware and software solutions.
The versatility of Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from home automation to industrial monitoring. By leveraging this tool, users can enhance the functionality of their IoT projects while maintaining control over their devices.
With its growing popularity, it's essential to understand the fundamentals of Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT and how it can be implemented effectively. This section will provide an overview of its capabilities and benefits.
Understanding Raspberry Pi Basics
What is Raspberry Pi?
Raspberry Pi is a small, affordable computer that can be used for a variety of purposes, including IoT development. It was first introduced in 2012 and has since become a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Key features of Raspberry Pi include:
- Compact size and low power consumption
- Compatibility with various operating systems
- Extensive community support and resources
Why Use Raspberry Pi for IoT?
Raspberry Pi is an excellent choice for IoT projects due to its flexibility, affordability, and ease of use. It allows developers to create complex systems with minimal hardware requirements, making it ideal for both beginners and experts.
Some of the advantages of using Raspberry Pi for IoT include:
- Wide range of input/output (I/O) options
- Support for multiple programming languages
- Integration with cloud platforms for remote access
What is RemoteIoT?
RemoteIoT refers to the ability to control and monitor IoT devices from a remote location. This technology enables users to interact with their devices without being physically present, enhancing convenience and efficiency.
Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT combines the power of Raspberry Pi with remote access capabilities, allowing users to manage their IoT projects from anywhere in the world. By leveraging this technology, developers can create innovative solutions that address real-world challenges.
Some of the key benefits of Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT include:
- Real-time monitoring and control of IoT devices
- Enhanced scalability and flexibility for IoT projects
- Improved security through advanced authentication and encryption
Setting Up Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
Hardware Requirements
Before setting up Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT, ensure you have the necessary hardware components. These include:
- Raspberry Pi board (Model 3 or later recommended)
- MicroSD card with pre-installed operating system
- Power supply and appropriate cables
Software Setup
Once the hardware is in place, proceed with the software setup. This involves installing the operating system and configuring the necessary settings for remote access.
Steps to set up Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT include:
- Download and install the Raspberry Pi OS on your microSD card
- Enable SSH and configure Wi-Fi settings in the boot folder
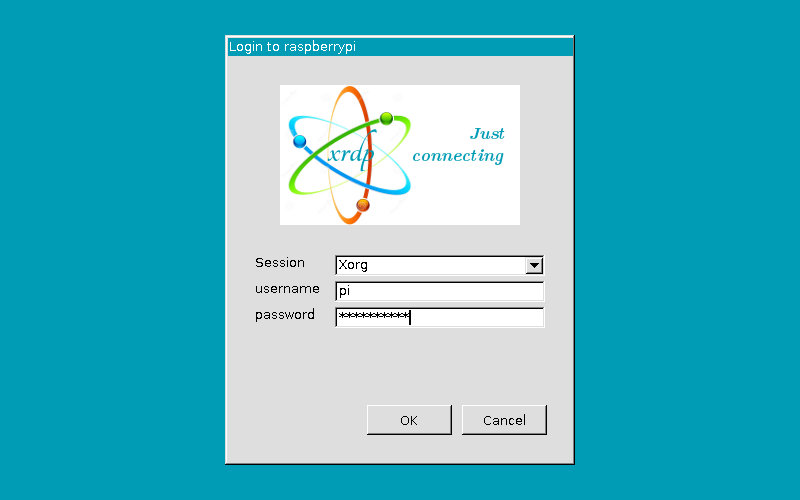
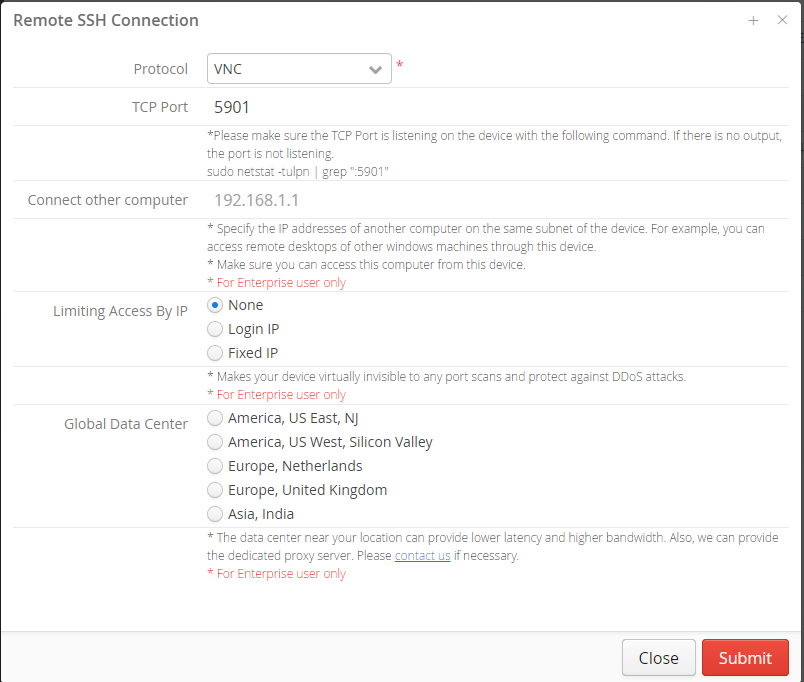
- Connect to your Raspberry Pi using a remote access tool such as PuTTY
Applications of Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT can be applied to a wide range of projects, from simple home automation systems to complex industrial monitoring solutions. Below are some of the most common applications:
- Smart home devices: Control lighting, thermostats, and security systems remotely
- Environmental monitoring: Track temperature, humidity, and air quality in real-time
- Industrial automation: Monitor and control machinery and production processes
With its versatility, Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT offers endless possibilities for innovation and development.
Security Considerations in Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
Best Practices for Securing Your Raspberry Pi
When implementing Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT, it's crucial to prioritize security to protect your devices and data. Follow these best practices to enhance the security of your setup:
- Change default passwords and use strong, unique credentials
- Enable a firewall and configure it to restrict unnecessary access
- Regularly update the operating system and installed software
Encryption and Authentication
Implementing encryption and authentication measures is vital for securing your Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT setup. Consider using:
- SSH for secure remote access
- SSL/TLS for encrypted communication between devices
- Two-factor authentication for additional security
Optimizing Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT Performance
To get the most out of your Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT setup, it's important to optimize its performance. This involves fine-tuning hardware and software settings to ensure optimal functionality.
Tips for optimizing Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT performance include:
- Use a lightweight operating system to reduce resource usage
- Disable unnecessary services and background processes
- Optimize code and scripts for efficiency and speed
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While setting up and using Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT, you may encounter various challenges. Below are some common issues and their solutions:
- Connection problems: Check network settings and ensure SSH is enabled
- Performance issues: Close unnecessary applications and free up disk space
- Software errors: Update the operating system and reinstall problematic packages
Essential Tools for Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
To streamline your Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT development process, consider using the following tools:
- Remote access tools: PuTTY, SSH, and VNC
- Programming environments: Python, Node-RED, and C++
- Monitoring software: Grafana, InfluxDB, and Mosquitto
These tools can enhance your productivity and help you create more efficient IoT solutions.
The Future of Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT
As technology continues to evolve, the potential applications of Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT are expanding rapidly. With advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and edge computing, the possibilities for innovation are endless.
Looking ahead, Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT is expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of IoT. Its ability to connect and control devices remotely will continue to drive progress in various industries, from healthcare to manufacturing.
Conclusion
Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT offers a powerful and versatile solution for IoT enthusiasts and professionals. By understanding its capabilities and implementing best practices, you can unlock its full potential and create innovative projects that address real-world challenges.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site to deepen your knowledge of IoT and related technologies. Together, let's continue to push the boundaries of what's possible with Raspberry Pi RemoteIoT.
References: