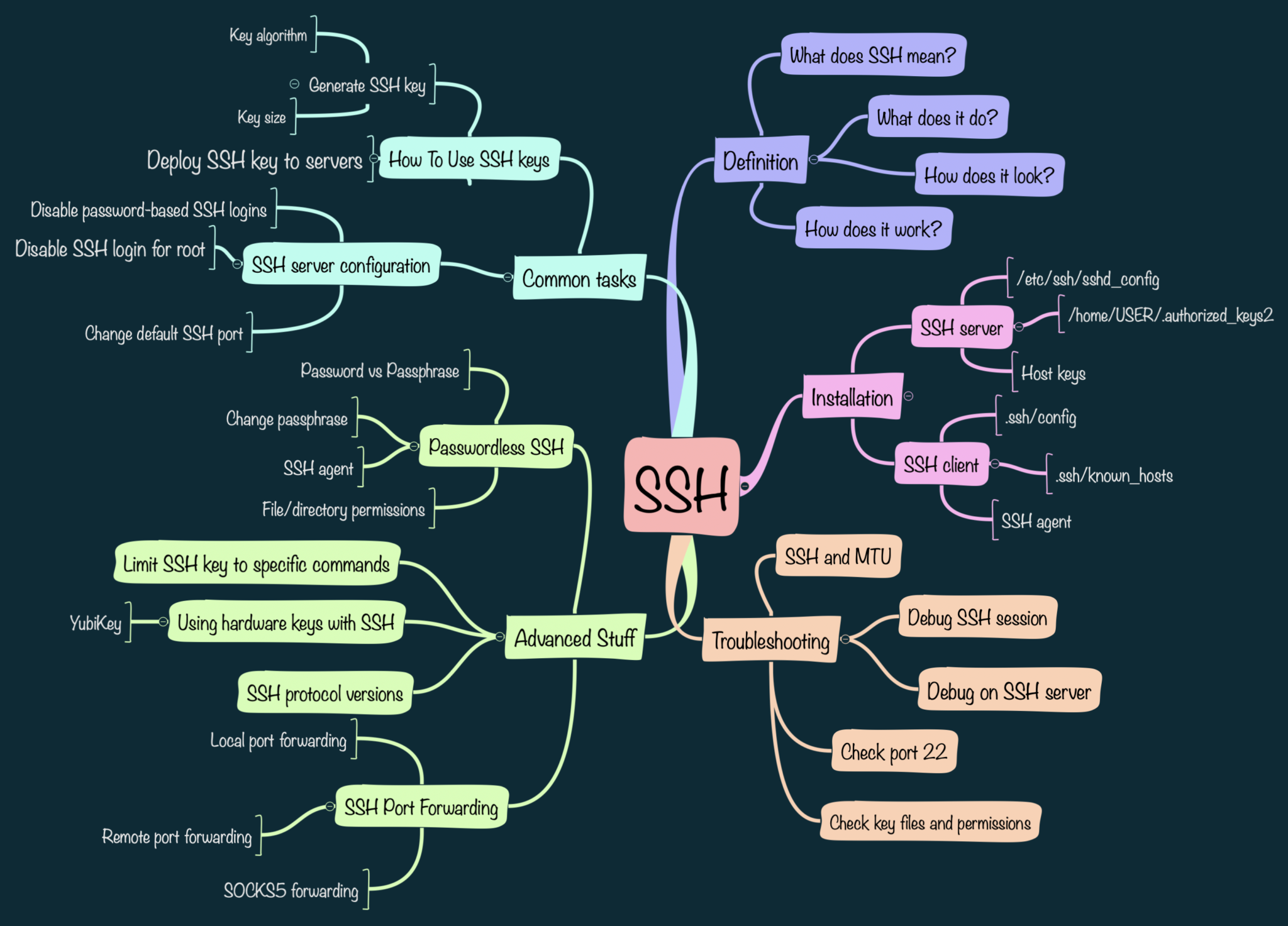
In today's interconnected world, IoT devices have become integral to both personal and professional environments. Managing these devices remotely through SSH (Secure Shell) is crucial for ensuring security and efficiency. This SSH remoteIoT tutorial will provide you with a detailed guide on how to securely manage IoT devices from anywhere.
As more organizations and individuals rely on IoT technologies, understanding SSH and its role in remote management becomes essential. This tutorial aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to set up and maintain secure connections for IoT devices.
Whether you're a beginner or an experienced professional, this guide will cover everything you need to know about SSH remoteIoT setup, configuration, and troubleshooting. Let's dive in!
Table of Contents
- Introduction to SSH
- Understanding RemoteIoT
- Why Use SSH for RemoteIoT?
- Biography of SSH
- Setting Up SSH on RemoteIoT
- Securing SSH Connections
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Best Practices for SSH RemoteIoT
- Case Studies and Examples
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to SSH
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol designed for secure remote communication and file transfer between devices. It provides a secure channel over an unsecured network by encrypting data and authenticating users.
In the context of remoteIoT, SSH serves as a robust solution for managing IoT devices without compromising security. Its ability to handle authentication, encryption, and integrity checks makes it indispensable for modern IoT ecosystems.
According to a report by Statista, the global IoT market is expected to reach $1.5 trillion by 2030, underscoring the growing importance of secure remote management solutions like SSH.
Understanding RemoteIoT
RemoteIoT refers to the practice of managing IoT devices from remote locations. This involves monitoring, configuring, and troubleshooting devices without physical access. RemoteIoT is essential for maintaining efficiency and security in IoT deployments.
Key benefits of RemoteIoT include:
- Improved operational efficiency
- Reduced downtime and maintenance costs
- Enhanced security through centralized management
SSH plays a pivotal role in enabling secure RemoteIoT operations by ensuring encrypted communication and secure access to devices.
Why Use SSH for RemoteIoT?
SSH offers several advantages for managing IoT devices remotely:
- Security: SSH encrypts all data transmitted between the client and server, protecting sensitive information from interception.
- Authentication: SSH supports multiple authentication methods, including passwords, public key authentication, and certificate-based authentication.
- Portability: SSH is widely supported across various operating systems and platforms, making it versatile for diverse IoT environments.
By leveraging SSH for RemoteIoT, organizations can ensure that their IoT infrastructure remains secure and operational even when accessed remotely.
Biography of SSH
SSH was originally developed in 1995 by Tatu Ylönen, a researcher at the Helsinki University of Technology, as a response to a password-sniffing attack on the university's network. Since then, SSH has evolved into a widely adopted standard for secure remote communication.
Below is a summary of SSH's key milestones:
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1995 | Development of SSH by Tatu Ylönen |
| 1997 | Release of SSH-1 protocol |
| 1998 | Release of SSH-2 protocol |
| 2006 | Standardization of SSH by Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) |
Setting Up SSH on RemoteIoT
Step 1: Install SSH Server
The first step in setting up SSH for RemoteIoT is installing an SSH server on your IoT device. Most Linux-based IoT devices come with OpenSSH pre-installed, but if not, you can install it using the following command:
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
Ensure that the SSH service is running by executing:
sudo systemctl status ssh
Step 2: Configure SSH
Once the SSH server is installed, configure it to meet your security requirements. Edit the SSH configuration file located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config.
Key configuration options include:
- Disabling password authentication
- Enabling public key authentication
- Changing the default SSH port
After making changes, restart the SSH service using:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Securing SSH Connections
Securing SSH connections is critical for protecting your IoT devices from unauthorized access. Here are some best practices:
- Use Strong Passwords: If password authentication is enabled, ensure that all passwords are strong and unique.
- Implement Public Key Authentication: Public key authentication eliminates the need for passwords, reducing the risk of brute-force attacks.
- Limit Access: Restrict SSH access to specific IP addresses or networks using firewall rules.
Additionally, consider using tools like fail2ban to automatically block malicious IP addresses attempting to access your SSH server.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite careful setup and configuration, issues may arise when using SSH for RemoteIoT. Below are some common problems and their solutions:
- Connection Refused: Ensure that the SSH service is running and that the correct port is being used.
- Authentication Failed: Verify that the correct credentials or keys are being used for authentication.
- Timeout Errors: Check network connectivity and ensure that firewall rules allow SSH traffic.
For more advanced troubleshooting, review the SSH server logs located at /var/log/auth.log.
Best Practices for SSH RemoteIoT
To maximize the effectiveness of SSH for RemoteIoT, adhere to the following best practices:
- Regularly update SSH software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Monitor SSH access logs for suspicious activity.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
By following these practices, you can ensure that your SSH-based RemoteIoT setup remains secure and reliable.
Case Studies and Examples
Several organizations have successfully implemented SSH for RemoteIoT management. For instance, a smart agriculture company used SSH to remotely monitor and control irrigation systems, reducing water waste by 30%.
Another example is a healthcare provider that employed SSH to securely manage IoT devices in hospitals, ensuring patient data remained protected while enabling efficient device management.
These case studies highlight the versatility and effectiveness of SSH in various industries.
Conclusion and Next Steps
This SSH remoteIoT tutorial has provided a comprehensive overview of using SSH for secure IoT device management. By understanding the fundamentals of SSH, setting it up correctly, and adhering to best practices, you can ensure that your IoT infrastructure remains secure and efficient.
We encourage you to:
- Leave a comment sharing your experiences with SSH for RemoteIoT.
- Explore additional resources on SSH and IoT security.
- Subscribe to our newsletter for more insightful content.
Stay informed and take proactive steps to enhance the security of your IoT ecosystem. Together, we can build a safer and more connected world.